Addressing Mortons Neuroma
Overview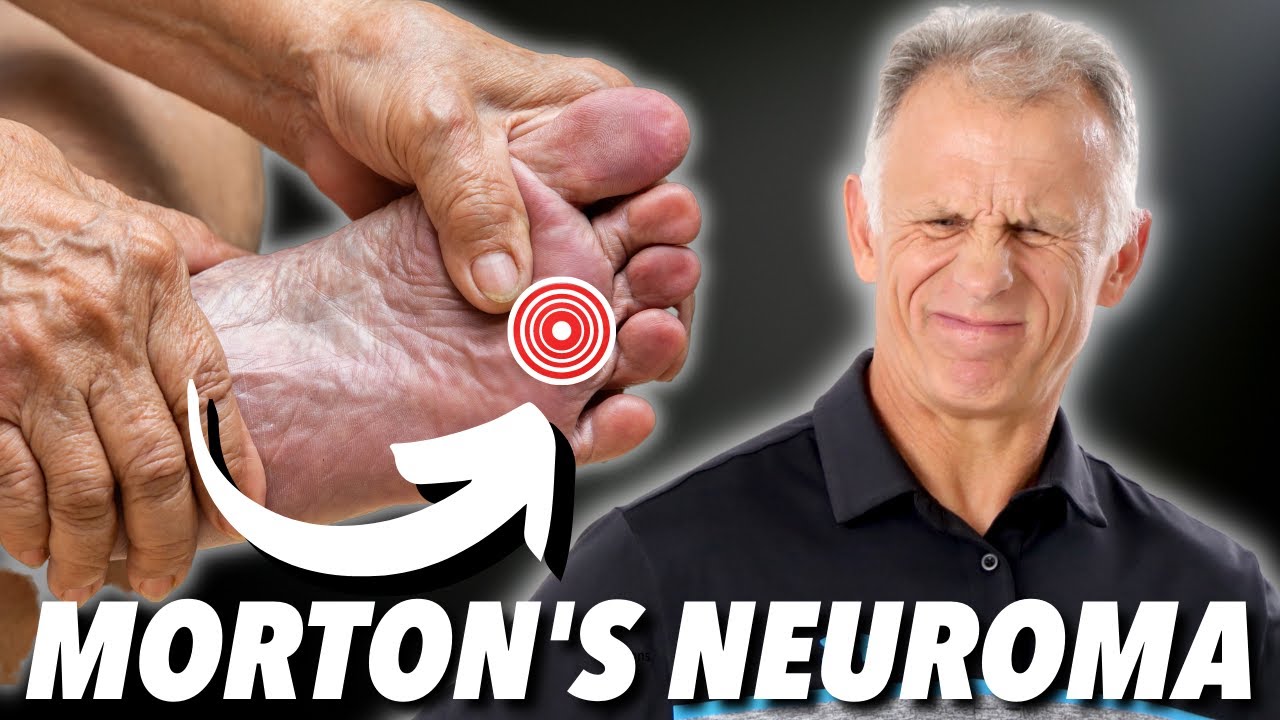 Morton's neuroma is a condition that affects one of the nerves that run between the long bones (metatarsals) in the foot. The exact cause is not certain. Symptoms include pain, burning, numbness and tingling between two of the toes of the foot. About a quarter of people just need simple treatments including modification of their footwear. Sometimes surgery is needed for long-standing (chronic) symptoms.
Morton's neuroma is a condition that affects one of the nerves that run between the long bones (metatarsals) in the foot. The exact cause is not certain. Symptoms include pain, burning, numbness and tingling between two of the toes of the foot. About a quarter of people just need simple treatments including modification of their footwear. Sometimes surgery is needed for long-standing (chronic) symptoms.Causes
Occupational hazards. Individuals whose jobs place undue stress on their forefeet (with or without wearing improper footwear) are among those who complain of neuromas. Podiatric physicians report that individuals who work on ladders, or who perform activities on their knees (such as doing landscaping, carpeting, flooring, or other work on the ground) are at risk for this problem, too, since these activities cause stress to the nerve near the ball of the foot. Those who engage in high-impact activities that bring repetitive trauma to the foot (running, aerobics, etc.) have a better than average chance of developing a neuroma at the site of a previous injury. To put it more simply, if you have sustained a previous injury to your foot (a sprain, stress fracture, etc.), that area of your foot will be more prone to neuroma development than an area that has not been injured. However, sports injuries aren?t automatically a ticket to neuromas. Trauma caused by other forms of injury to the foot (dropping heavy objects, for example) can also cause a neuroma to develop at the site of the previous injury. Much though we hate to say it, sometimes neuromas just develop and nobody knows why. The patient doesn?t have a previous injury, is wearing properly fitted shoes, and doesn?t stress his/her feet with any specific activity but the neuroma develops anyway. It is important to remember that some of the factors listed above can work alone, or in combination with each other, to contribute to the formation of neuroma.
Symptoms
Symptoms associated with a neuroma include a dull burning sensation radiating towards the toes, a cramping feeling, or even a stinging, tingling sensation that can be described as being similar to an electric shock. It is often worse when wearing shoes with most people finding the pain disappears when removing their shoes.
Diagnosis
To confirm the diagnosis, your doctor will examine your feet. He or she will look for areas of tenderness, swelling, calluses, numbness, muscle weakness and limited motion. To check for a Morton's neuroma, your doctor will squeeze the sides of your foot. Squeezing should compress the neuroma and trigger your typical pain. In some cases, your doctor will find numbness in the webbed area between the affected toes. Pain in two or more locations on one foot, such as between both the second and third toes and the third and fourth toes, more likely indicates that the toe joints are inflamed rather than a Morton' neuroma.
Non Surgical Treatment
Rest. Continuing with normal training will increase pain and inflammation and prevent the injury from healing. Wear a metatarsal pad under the forefoot which will raise and spread the bones of the forefoot taking the pressure off the nerve. Wearing metatarsal pads in the shoes under the forefoot spreads the metatarsals creating more space for the nerve. See a sports injury professional who can advise on treatment and rehabilitation. Orthotic inserts may be required to correct any biomechanical dysfunction of the foot.
Surgical Treatment
If conservative treatments haven't helped, your doctor might suggest injections. Some people are helped by the injection of steroids into the painful area. In some cases, surgeons can relieve the pressure on the nerve by cutting nearby structures, such as the ligament that binds together some of the bones in the front of the foot. Surgical removal of the growth may be necessary if other treatments fail to provide pain relief. Although surgery is usually successful, the procedure can result in permanent numbness in the affected toes.